Sickle Cell Disease
The term, sickle cell disease, refers to a group of inherited blood disorders. People have sickle cell disease from birth. It occurs when a person inherits one sickle cell gene from each parent.
Sickle cell disease primarily affects those of African ancestry, but can also affect those of Hispanic, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and South Asian descent.
What is Sickle Cell Disease ?
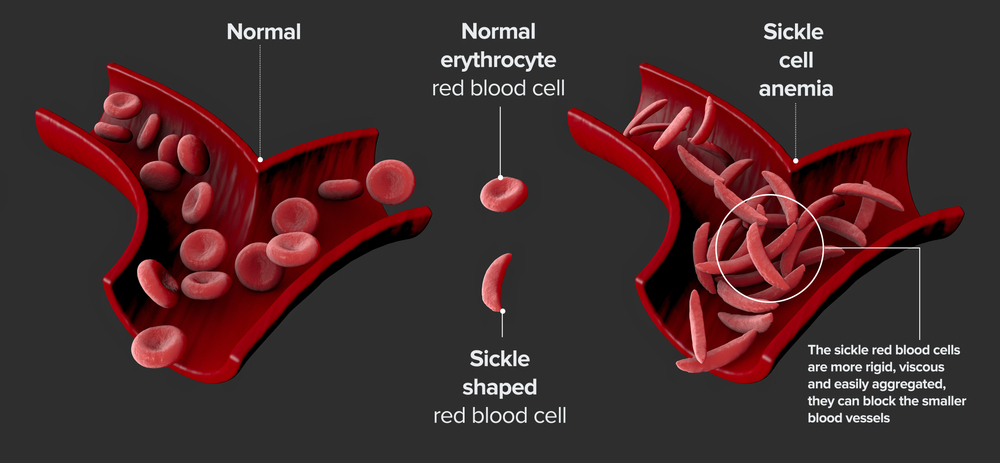
Sickle cell disease affects hemoglobin — a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body. This inherited blood disorder causes the body to produce abnormal hemoglobin, causing the red blood cells to develop the sickle, or crescent, shape associated with the disease.
Sickle cells are rigid and sticky. They become lodged in blood vessels, blocking proper blood flow. This blockage can cause serious complications.
Sickle cell disease and anemia
You may have heard people interchange the terms sickle cell anemia and sickle cell disease. This is not entirely accurate.
“In rare circumstances — such as severe dehydration, extreme physical exertion, or exposure to very high altitude — persons with sickle cell trait may develop complications similar to those of sickle cell disease.”
Sickle Cell Disease Symptoms and Complications
- Excruciating pain crises
- Serious infections
- Damage to vital organ systems
- Pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs’ blood vessels) Stroke
- Severe anemia
Millions of people across the world are living with sickle cell disease. The struggles they face are real, but their voices often go unheard. In this docuseries, see how these passionate people find ways to thrive and achieve their goals.
Millions of people across the world are living with sickle cell disease. The struggles they face are real, but their voices often go unheard. In this docuseries, see how these passionate people find ways to thrive and achieve their goals.